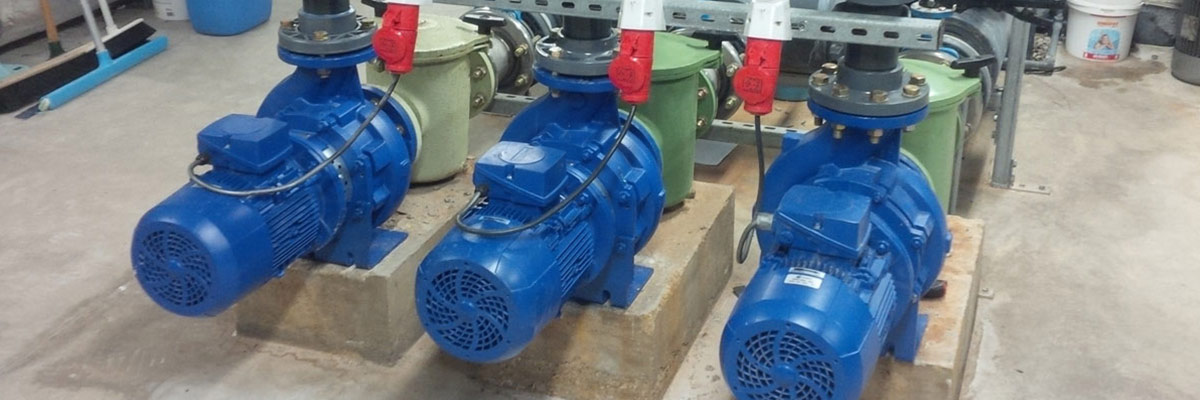
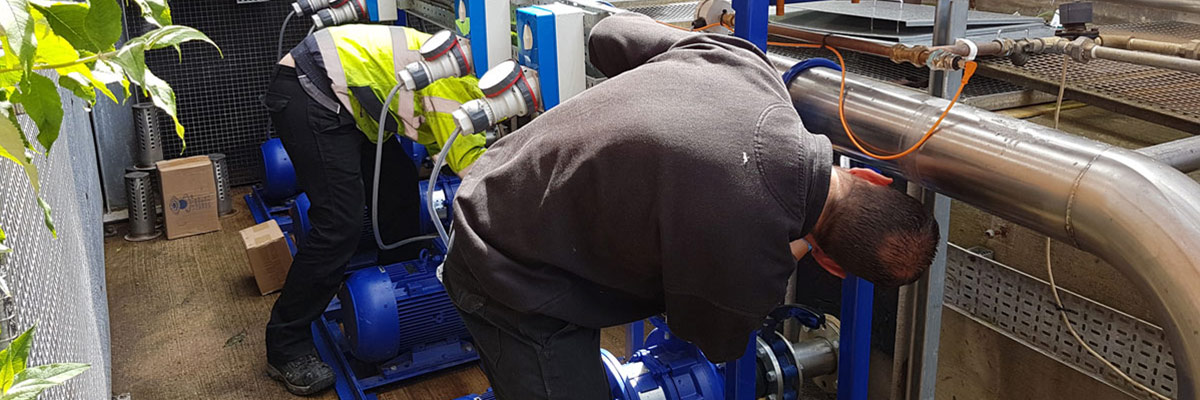
A self-priming pump uses a water and air mixture in order to fully prime the pump.
While called a self-priming pump, it is actually a centrifugal pump in principle. It uses centrifugal force to create a pumping action by using a pressure differential in a liquid, and a suction in the priming chamber. The impeller draws the fluid into the pump and displaces it out of the discharge port. The movement of this fluid creates a suction, lifting the water from the sump below into the pump, starting the pumping action.
What is priming: Priming is filling the intake with water/liquid to displace the air in the system, to
create a vacuum, to suck up the fluid from beneath the pump.
As all the air is displaced, the liquid continues to mix with the air that is coming up the suction line. This creates a vacuum on the suction line, and the liquid is forced up the suction line due to
atmospheric pressure and enters the impeller. This continual process keeps the pump operating.
When the pump stops, a non return valve, within the pump maintains water within the priming chamber, keeping it primed and ready for operating again. Liquid must always be present in the priming chamber to allow the pump to work automatically.
On initial install or after maintenance, this priming chamber has to be filled with the liquid to start the process.
Maintenance is carried out above ground, due to no submerged parts, making it quick and easy.
Positive displacement pumps can be used for self priming, for example: Lobe pumps, progressive cavity pumps, diaphragm pumps, twin screw pumps, eccentric pumps and peristaltic pumps. The positive displacement pumps are typically used in hygienic applications or for liquid with a high viscosity. For further details on these pumps, refer to their own product page.
Self priming Pumps are generally suited to transfer and high flow applications. Pressure can be limited as they typically only have one impeller. Multistages are available to overcome this. The most common uses include water, sewage, agriculture, petroleum and petrochemical pumping. Centrifugal pumps are often chosen for their high flow rate capabilities, abrasive solution compatibility, mixing potential, as well as their relatively simple engineering.
Typical use for these pumps are:
- Waste water
- Cooling water pumps
- Water transfer pumps
- General industrial pumps
- Process pumps
- Dewatering
- Swimming pool pumps











 Solve your water pressure problems today, call 01604 648 800
Solve your water pressure problems today, call 01604 648 800